Are you finding yourself wrestling with the intricacies of connecting your Internet of Things (IoT) devices to a remote desktop, specifically on a Mac, and feeling a sense of frustration? You're not alone, and the path to a seamless connection is closer than you think.
The journey of connecting IoT devices to a remote desktop via a router on a Mac can indeed be a source of headaches. The reasons for this are varied and often complex. The good news is, by understanding the underlying issues and applying a systematic approach, you can transform this challenge into an efficient, reliable system. Consider this guide your definitive resource. Whether you're a seasoned tech enthusiast or just starting to delve into the world of IoT, this article will provide you with the knowledge and tools you need to overcome the hurdles and establish a robust remote desktop connection.
Many users find themselves in similar situations. Establishing remote connections to IoT devices on a Mac, particularly when these devices are located behind a router, presents a set of challenges. These range from network configurations to software glitches. This is especially true for those using macOS. The complexities can involve port forwarding, firewall settings, and the specific configurations of your network environment. Yet, with the right guidance, these seemingly complex issues can be navigated with relative ease.
Before diving deep into the troubleshooting, let's start with the basics. One common scenario is the challenge of accessing your IoT devices remotely, especially when they are behind a router. Let's assume that the specific device you are trying to connect is a smart thermostat, designed to monitor and adjust the temperature of a house. The thermostat, like many IoT devices, connects to your home network through a Wi-Fi router.
The objective is to establish a secure and efficient remote desktop connection to this thermostat, allowing you to monitor the temperature, change settings, or troubleshoot issues even when you are not physically present at the location. This involves the router, which acts as a gateway between your local network (where the thermostat resides) and the internet. To access the thermostat remotely, you need to configure the router to forward specific traffic to the thermostat.
Now, consider the difficulties that might arise. Your thermostat has become unresponsive, and you need to diagnose the problem. Perhaps, the connection drops frequently, or you are unable to connect at all. Or the settings are difficult to configure because of the complexities of the router, and your specific macOS setup. This is where a deep understanding of the remote desktop configuration, including port forwarding, network settings, and security measures, becomes essential.
This comprehensive guide is tailored to address these issues. It will take you step-by-step through the configuration process, with troubleshooting tips to solve the common problems. By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of how to resolve remote desktop connectivity issues on your Mac.
Let's break down the most common culprits behind the frustrating scenario of remote access failures. The possibilities are wide-ranging: network configurations, software glitches, and the intricacies of your particular macOS setup all play a role. Let's delve into the frequently encountered problems that disrupt our remote access and understand them.
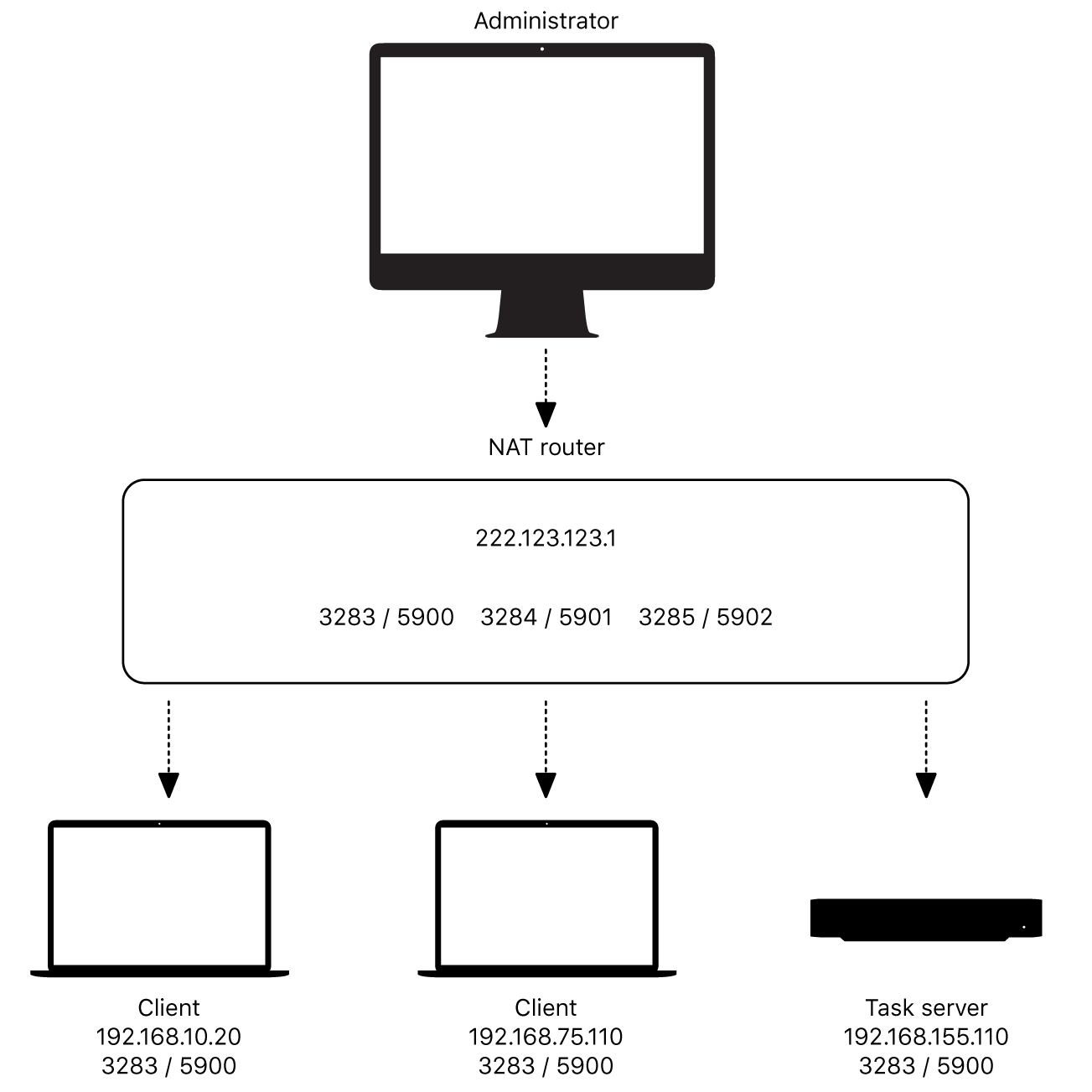
First and foremost, let's address the network configurations. Routers, the gatekeepers of your home or business network, play a crucial role in determining whether your IoT devices can be accessed remotely. Your router needs to be correctly configured to allow outside devices to connect to your IoT devices. This usually involves a process called "port forwarding." Think of port forwarding as a system of directing traffic through your router. When traffic from a specific port on the internet reaches your router, it knows to direct it to a particular device on your local network. If port forwarding is not configured correctly, your remote access will simply fail.
Next, let's consider the security aspect. When you're setting up remote access, it's crucial to protect your devices from potential threats. Weak passwords, outdated software, or even misconfigured firewalls can leave your devices vulnerable to intrusion. Implementing strong security measures, such as robust passwords, regularly updating your software, and properly configuring your firewall, helps ensure that only authorized users can access your devices.
Software glitches and system compatibility pose additional problems. It's common for remote desktop software or macOS itself to experience glitches. Outdated software or incompatible versions might block remote access, or even worse, create security vulnerabilities. Keeping your software up-to-date and ensuring compatibility with your IoT devices is critical for seamless operation.
Now, let's talk about the specific steps involved in setting up a remote desktop connection for your IoT devices on a Mac. The process can be broken down into several stages, including choosing the right remote desktop software, configuring your router, and setting up your macOS device. We will delve into each of these stages, providing detailed, step-by-step instructions, and practical advice to help you successfully navigate the setup process.
Many users face challenges when trying to establish secure and efficient remote connections for their IoT devices. Thats why it is so important to choose the right tools. macOS offers a built-in remote desktop solution called "Screen Sharing," which is a viable starting point. There are also several third-party applications available, like VNC Connect or TeamViewer, each with its own benefits and drawbacks. These different tools offer varied features, security protocols, and ease of use. Selecting the right remote desktop software is a fundamental first step, and the one that best suits your needs will make all the difference.
Once you have selected your remote desktop software, you will need to configure your router to allow remote access. As mentioned earlier, this usually involves setting up port forwarding. You will need to access your router's configuration interface. It often entails entering your router's IP address into a web browser and then logging in with your administrator credentials. Within the router's settings, you will find the port forwarding section. Here, you will need to specify the port number that the remote desktop software uses (e.g., 5900 for VNC) and the IP address of your IoT device on your local network.
Next, you will need to configure your macOS device to accept remote connections. This step depends on which remote desktop software you are using. If you're using the built-in Screen Sharing, you will need to enable screen sharing in System Preferences under the "Sharing" option. Then, you will need to set up a password to secure the remote access. If you use a third-party application, you will usually need to install the software on your Mac and configure it according to the software's instructions.
Now, let's talk about troubleshooting common issues. Even with a well-laid-out setup, problems can still occur. One common problem is a failure to connect to your remote desktop. This could be due to incorrect network settings, the wrong IP address, or firewall issues. Always start by verifying your network settings. Double-check that your router's port forwarding is correctly configured, ensuring that the correct port number is directed to the correct IP address. Check the IP address of your IoT device. Ensure that you are using the correct IP address for your IoT device on your local network.
Another common problem is the failure of the remote desktop connection to maintain stability. If you experience frequent disconnects, it might be due to a weak internet connection, a problem with your router, or issues related to your remote desktop software. Make sure that your internet connection is stable and that your router is functioning correctly. Try restarting your router and your IoT device, and test a stable connection.
For those facing specific issues with VNC connections behind a firewall, troubleshooting is crucial. This involves checking firewall settings on both your Mac and your router. Make sure that the firewall on your Mac isn't blocking the VNC connections. You might need to create an exception for the VNC application in your firewall settings. Additionally, you should also check the firewall settings on your router and confirm that it isn't blocking the VNC traffic.
Let's delve into the more advanced solutions for those facing persistent remote desktop connectivity issues on Mac, going beyond the basics. Sometimes, the standard troubleshooting steps are not enough. This is where we can utilize tools and strategies to address the complex problems that can disrupt your remote connections. This may involve advanced port forwarding, the use of a Dynamic DNS (DDNS) service, or establishing a secure virtual private network (VPN).
Advanced port forwarding becomes necessary when you are experiencing conflicts or have multiple IoT devices behind the same router. If you have multiple IoT devices, each of which requires remote access, and your router only allows you to forward one port to each device, you may encounter a conflict. One solution is to set up a different port for each device in your router's port forwarding settings. You'll then need to remember which port corresponds to which device when you establish the remote connection.
For those with dynamic IP addresses, employing a DDNS service is vital. Your internet service provider (ISP) might give you a dynamic IP address, which means your IP address changes regularly. This can disrupt your remote connections, because you would need to update the IP address every time it changes. A DDNS service, like No-IP or DynDNS, will provide you with a static hostname that points to your current dynamic IP address. You can then use the static hostname to connect to your devices, even if your IP address changes.
For enhanced security and flexibility, using a VPN to connect to your remote desktop is a great idea. A VPN creates an encrypted connection between your Mac and your local network, providing an extra layer of security and allowing you to access your devices as if you were on the local network. Set up a VPN server on your router or a separate device on your local network. Then, configure your Mac to connect to the VPN server before attempting a remote desktop connection. This is particularly useful when you want to access your IoT devices over a public Wi-Fi network.
Furthermore, there are often questions regarding how to deal with remote login issues over the internet. If you find that you cannot connect to your devices remotely, it's likely related to a network configuration issue, such as incorrect port forwarding, firewall restrictions, or an unstable internet connection. Double-check your router's settings, including the port forwarding configuration, and ensure that the correct ports are open and directed to the correct devices. Also, verify that your firewall isn't blocking any connections.
Addressing frequently asked questions (FAQs) will give a deeper understanding of remote login issues over the internet and help you resolve them. One common question is: "Why can't I connect to my IoT devices remotely, even after setting up port forwarding?" The primary reason is that your router might be configured improperly. Double-check the port numbers that you have set in your router, as well as the IP address of the device. Also, it is important to verify that the firewall on your Mac and the router aren't blocking connections.
Another common issue is "Can I access my IoT devices if my IP address changes?" This is an essential question, and the answer is that it depends on the type of internet connection you have. If you have a dynamic IP address, which changes regularly, using a DDNS service is important. It provides a static hostname that you can use to connect to your devices, even if your IP address changes. If you have a static IP address, then the problem becomes simpler.
Another question is: "What are the best security practices to ensure my IoT devices are secure?" The most important thing is to use strong passwords, update software, and secure your router's settings. Change the default password on your router, use a strong password for your remote desktop connections, and update your remote desktop software and any other software running on your devices.
Resolving remote login issues involves a systematic approach that addresses network settings, software updates, compatibility issues, and security measures. The first step is to check the basic network settings, including the IP addresses of your devices and the port forwarding settings on your router. Make sure that the correct ports are open, and verify that the correct IP addresses are being used. Keep the software updated, as the latest updates often include fixes for known vulnerabilities and performance improvements. Make sure that your remote desktop software and the operating systems are compatible with the IoT devices. Make sure to follow security best practices. Use strong passwords, update your software regularly, and implement additional security features, such as multi-factor authentication, if possible. By following this approach, you can ensure that your remote desktop setup functions correctly.
Are you experiencing difficulties with VNC connections behind a firewall on your Mac? If you find that you cant establish a VNC connection to your IoT devices, a firewall might be the culprit. Check the firewall settings on both your Mac and your router. Make sure that the firewall on your Mac isn't blocking VNC connections, and that the router's firewall isn't blocking VNC traffic. You might have to create an exception in your firewall settings to allow the VNC application. The other step is to check the router's firewall settings and make sure that it isn't blocking the VNC traffic.
If the steps above haven't resolved the problem, there are a few advanced techniques that you could try. These could include setting up a VPN, testing your network connection, and using different VNC clients. A VPN creates an encrypted connection between your Mac and your local network, and it improves security and can sometimes resolve connectivity problems. Test your network connection. Sometimes, the issue isn't with the settings or the devices, but with a problem with the internet connection. Use different VNC clients. If one client isn't working, try another one. There are many different VNC clients available, and it's possible that one will work better than others.
Many users face challenges when integrating internet of things (IoT) devices with remote desktop solutions on macOS. Whether it's connectivity issues, configuration errors, or compatibility problems, troubleshooting these problems requires a systematic approach. Remember, the solutions lie in understanding your network, your devices, and the software you are using. With the right knowledge and persistence, any connectivity issue can be resolved.